How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate data collection. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, covering everything from understanding basic drone components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight techniques and adhering to safety regulations. We’ll explore the nuances of drone controls, delve into the art of capturing stunning aerial visuals, and equip you with the knowledge to troubleshoot common issues.
Prepare to take flight!
We will cover essential topics such as understanding your drone’s components and their functions, conducting thorough pre-flight checks, mastering basic and advanced flight maneuvers, capturing high-quality aerial media, performing routine maintenance, and understanding the legal and safety aspects of drone operation. By the end of this guide, you’ll possess the confidence and expertise to handle your drone responsibly and effectively.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the different parts of your drone and the associated terminology is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will break down the key components and define common terms used in drone piloting.
Drone Components and Their Functions

A drone is comprised of several essential components working in concert. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight and functionality.
| Component | Function | Troubleshooting Tips | Safety Precautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust for lift and maneuverability. | Inspect for damage before each flight; replace damaged propellers immediately. | Ensure propellers are securely fastened; keep hands and fingers clear of rotating propellers. |
| Motors | Power the propellers; responsible for the drone’s movement. | Check motor connections; consider professional repair if a motor malfunctions. | Avoid overloading the motors; land immediately if a motor shows signs of failure. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone; processes data from sensors and controls the motors. | Calibrate the flight controller regularly; update firmware as needed. | Protect the flight controller from impacts; avoid exposing it to water or extreme temperatures. |
| Battery | Provides power to all drone components. | Always use a fully charged battery; monitor battery levels during flight. | Handle batteries carefully; avoid short-circuiting or overheating. |
| GPS Module | Provides location data for precise positioning and autonomous flight modes. | Ensure a clear view of the sky for optimal GPS signal reception; recalibrate if necessary. | Avoid flying in areas with weak GPS signals. |
| Camera | Captures photos and videos. | Keep the lens clean; adjust settings based on lighting conditions. | Protect the camera from impacts and extreme temperatures. |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Stabilizes the camera for smooth footage. | Ensure the gimbal is properly calibrated; avoid jarring movements. | Handle with care; avoid dropping or applying excessive force. |
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms will enhance your understanding and ability to troubleshoot issues.
- Altitude Hold: A feature that maintains a constant altitude.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mount for the camera.
- Payload: The weight the drone can carry (e.g., camera, sensor).
- Return-to-Home (RTH): A feature that automatically returns the drone to its starting point.
- Waypoint Navigation: Programming the drone to fly to a series of pre-defined points.
- Firmware: The software that controls the drone’s functions.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Controls the speed of each motor.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety protocols and legal considerations, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to ensure safe and responsible flight. Ultimately, proficient drone piloting comes from practice and a thorough understanding of the technology.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for ensuring a safe and successful flight. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents and equipment damage.
Pre-Flight Checklist
- Check battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Inspect propellers for damage or wear.
- Verify all components are securely attached.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Acquire a strong GPS signal (indicated by sufficient satellites).
- Check for any obstructions in the flight area.
- Review local regulations and airspace restrictions.
Selecting a Safe and Legal Flight Location
Choosing the right location is paramount. Consider factors like proximity to obstacles, weather conditions, and legal airspace restrictions.
- Open areas with minimal obstacles are ideal.
- Avoid flying near airports, power lines, or crowds.
- Check for any local drone regulations or restrictions.
- Be aware of weather conditions; avoid flying in strong winds or rain.
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight process aids in ensuring all steps are followed consistently.
(Imagine a flowchart here: Start -> Battery Check -> Propeller Check -> Component Check -> Power On -> Calibration -> GPS Signal Acquisition -> Obstruction Check -> Regulations Check -> Flight)
Basic Drone Controls and Maneuvers: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding basic drone controls is fundamental to safe and efficient operation. This section covers essential maneuvers.
Basic Flight Controls
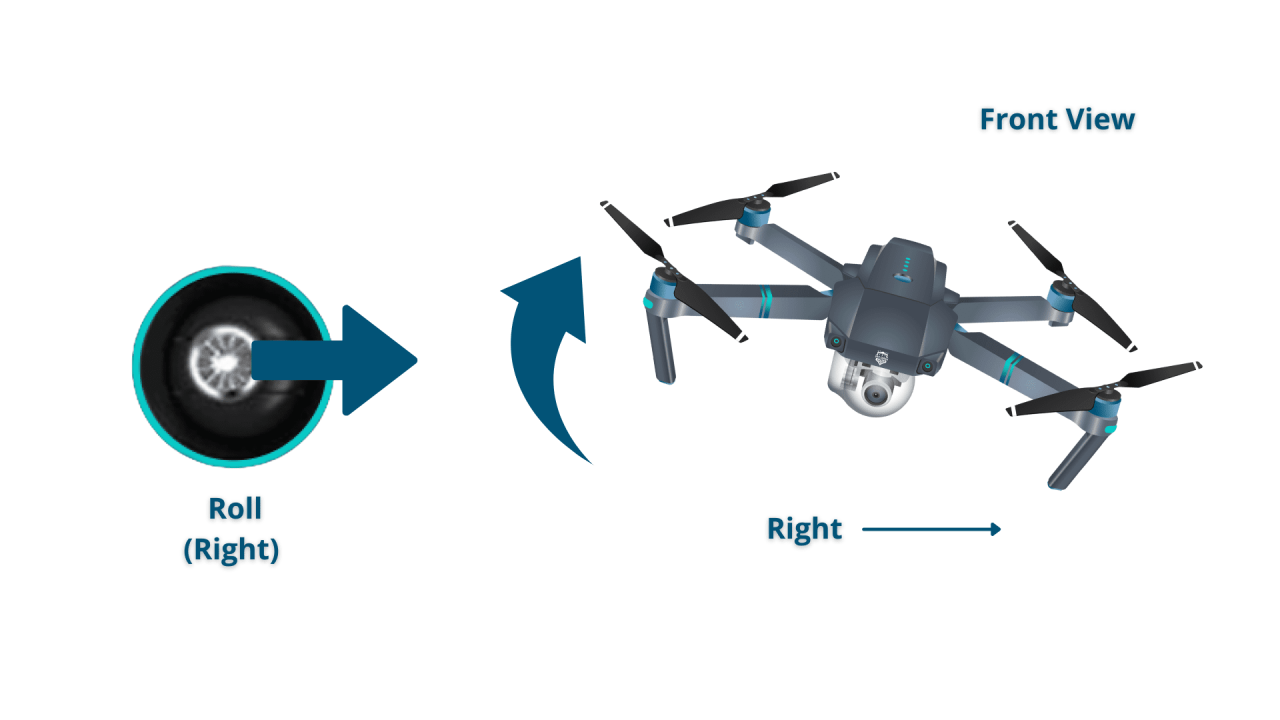
Most drones utilize a control system based on four axes: throttle, pitch, roll, and yaw.
- Throttle: Controls altitude (up and down).
- Pitch: Controls forward and backward movement.
- Roll: Controls left and right movement.
- Yaw: Controls rotation (turning left and right).
Flight Maneuvers
Practicing these maneuvers is key to developing proficiency.
- Hovering: Maintaining a steady position in the air.
- Ascending: Increasing altitude smoothly.
- Descending: Decreasing altitude gradually.
- Turning: Rotating the drone using the yaw control.
Control Interface Comparison
Different drone models may have varying control interfaces (e.g., joystick layout, button placement). Familiarization with your specific drone’s interface is crucial.
(This section would benefit from a table comparing the interfaces of a few popular drone models, but due to the lack of a specific request for models, a general description is provided instead.)
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Many drones use a standard joystick layout, with left stick controlling movement and right stick controlling camera orientation. However, some manufacturers incorporate custom features, and button configurations can vary.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Once comfortable with basic maneuvers, you can explore more advanced techniques to enhance your drone piloting skills.
Advanced Flight Techniques and Emergency Procedures
These techniques require practice and a solid understanding of basic controls.
- Waypoint Navigation: Pre-programming a flight path for autonomous flight.
- Circling: Flying in a circular pattern.
- Following a Specific Path: Precisely navigating a predefined route.
- Low-Battery Landings: Initiating an automated return-to-home (RTH) procedure upon low battery detection.
- Loss-of-Signal Scenarios: Understanding the drone’s fail-safe mechanisms (e.g., RTH activation).
Tips for Improving Flight Smoothness and Stability
- Practice smooth and controlled movements.
- Avoid abrupt changes in direction or altitude.
- Maintain awareness of wind conditions.
- Regularly calibrate your drone’s sensors.
- Utilize assisted flight modes (when available).
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and techniques. This section will cover key aspects.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
The quality of your footage depends on various factors, including camera settings, lighting, and composition.
- Use a high-quality camera (if applicable).
- Experiment with different shooting angles and perspectives.
- Adjust settings for optimal exposure and focus.
- Utilize the gimbal for smooth and stable shots (if applicable).
Adjusting Settings for Different Lighting Conditions
Lighting conditions significantly impact the quality of your photos and videos.
- Bright Sunlight: Reduce exposure to avoid overexposure.
- Overcast Conditions: Increase exposure to compensate for lower light levels.
- Low Light: Use a higher ISO setting and a wider aperture (if possible).
Camera Modes Comparison
| Camera Mode | Use |
|---|---|
| Photo | Capturing still images. |
| Video | Recording moving images. |
| Time-lapse | Creating a sequence of images over time. |
| Slow Motion | Recording video at a higher frame rate for slow-motion playback. |
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Proper maintenance and storage are vital for prolonging the lifespan of your drone. This section will Artikel best practices.
Cleaning and Maintaining Drone Components
Regular cleaning and maintenance prevent damage and ensure optimal performance.
- Clean the propellers and body with a soft cloth.
- Inspect for any loose screws or damaged parts.
- Clean the camera lens carefully.
- Store the battery in a cool, dry place.
Best Practices for Storage
Proper storage protects your drone from damage and extends its operational life.
- Store the drone in a dry, cool environment.
- Keep it away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Store the battery separately and ensure it’s not fully charged for extended periods.
- Use a protective case or bag for transport and storage.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions

- Problem: Drone won’t power on. Solution: Check battery level and connections.
- Problem: Propeller failure. Solution: Replace damaged propellers.
- Problem: GPS signal loss. Solution: Relocate to an area with better GPS reception.
- Problem: Low battery warning. Solution: Initiate RTH or land immediately.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount. This section addresses key safety considerations and legal requirements.
Key Safety Considerations
Prioritizing safety prevents accidents and ensures responsible drone operation.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Avoid flying near people or obstacles.
- Be aware of wind conditions.
- Check battery levels frequently.
- Follow all local regulations and guidelines.
Regulations and Legal Requirements
Drone regulations vary by location. Always check local laws and obtain necessary permits before flying.
(This section would require specific legal information relevant to a particular region, which is beyond the scope of this general guide. It’s crucial to research the laws in your area.)
Safe Drone Operation Poster
(Imagine a poster here. The poster would depict a drone in a safe flight environment, away from obstacles and people. Clear visuals would illustrate the importance of maintaining visual line of sight, checking battery levels, and adhering to local regulations. The poster would feature concise text highlighting key safety messages.)
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
This section provides guidance on resolving common drone malfunctions.
Common Drone Malfunctions, Causes, and Solutions, How to operate a drone
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, loose connections | Charge battery, replace battery, check connections |
| Propeller malfunction | Damaged propeller, loose propeller, motor failure | Replace propeller, tighten propeller, repair or replace motor |
| GPS signal loss | Obstructions, weak signal, GPS module malfunction | Relocate to open area, recalibrate GPS, contact manufacturer |
| Unstable flight | Wind conditions, calibration issues, motor imbalance | Avoid strong winds, recalibrate sensors, balance propellers |
| Unexpected movements | Calibration issues, interference, software glitches | Recalibrate, move away from interference sources, update firmware |
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical understanding and practical experience. This guide has provided a solid foundation in both, equipping you with the knowledge to safely and effectively pilot your drone. Remember, continuous practice and adherence to safety guidelines are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone operator. Embrace the possibilities, explore new heights, and capture the world from a unique perspective, always prioritizing safety and legal compliance.
Popular Questions
What is the best drone for beginners?
Several user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring intuitive controls and safety features. Research models with good reviews and consider factors like flight time and camera quality.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is crucial for accurate flight. It’s recommended to calibrate before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant impact.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to manual control and carefully bring it down to a safe landing. Avoid flying in areas with poor GPS reception.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by location. Check with your local aviation authority to determine if registration is mandatory and how to complete the process.
